
One of the prevalent reasons necessitating shoulder surgery is the treatment of impingement syndrome. This condition occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff are abnormally trapped and compressed during movement, resulting in ongoing damage to both the tendons and the bursa—cushioning structures within the joint space.
The shoulder comprises three primary bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the clavicle (collarbone). Understanding the intricacies of shoulder anatomy is crucial for accurately diagnosing its issues. The head of the upper arm bone is situated within a rounded socket known as the glenoid, which is part of the shoulder blade. Maintaining the proper alignment of the arm bone within this socket relies on a complex interplay of muscles and tendons, collectively known as the rotator cuff. These structures play a pivotal role in facilitating the intricate and precise movements of the shoulder joint.
Certainly, shoulder problems encompass various conditions that can affect the joint and surrounding structures. Here’s a detailed breakdown of some of the most common shoulder issues:
Tendon Inflammation (Bursitis or Tendinitis): This involves inflammation of the tendons (tendinitis) or the bursae (bursitis) in the shoulder. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the tendons and bones, reducing friction in the shoulder. Overuse, repetitive motions, injury, or underlying conditions like arthritis can lead to inflammation in these structures, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Tendon Tear: Tears in the tendons of the rotator cuff are quite common and can be either partial or complete tears. These tears can occur due to acute injury, degeneration over time, or as a result of chronic inflammation. Tendon tears often lead to pain, weakness, and restricted movement in the shoulder.
Instability (Labral Tear): The labrum is a ring of cartilage that lines and deepens the shoulder socket, providing stability to the joint. An injury or trauma can cause a tear in the labrum, leading to shoulder instability. This instability can cause discomfort, a sense of the shoulder “popping” out of place, and difficulty with certain movements.
Arthritis: Shoulder arthritis can develop due to wear and tear over time (osteoarthritis) or as a result of autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. It causes the cartilage covering the bones within the joint to wear away, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
Fracture (Broken Bone): Fractures in any of the bones that form the shoulder joint, such as the humerus, scapula, or clavicle, can occur due to trauma or injury. Fractures may require surgical intervention depending on the severity and location of the break.
Less common causes of shoulder problems include:
Tumors: Rarely, tumors can develop in the bones, soft tissues, or nerves of the shoulder, causing pain and affecting shoulder function.
Infection: Infections in the shoulder joint can occur but are relatively uncommon. They may result from surgery, injury, or systemic infections spreading to the shoulder.
Nerve-related Problems: Conditions like nerve impingement or compression can lead to shoulder pain, weakness, or numbness due to pressure on nerves in the shoulder region.
Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment by a healthcare professional are essential for effectively managing these shoulder issues, which can range from conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, and medications to surgical interventions in more severe cases.
The Conditions related to shoulder surgery in detail are
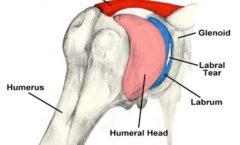
Labral Tear: Damage to the cartilage ring (labrum) in the shoulder joint, often caused by trauma or repetitive movements. Symptoms include pain, instability, and reduced range of motion. Treatment may involve rest, physical therapy, or surgical repair.
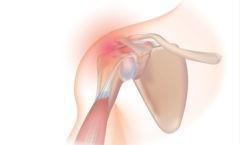
Rotator Cuff Tear: Injury to the tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint, leading to pain, weakness, and limited movement. Treatments range from rest and physical therapy to surgical repair, depending on severity.

Shoulder Osteoarthritis: Degenerative joint disease causing pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility in the shoulder due to cartilage breakdown. Treatment options include conservative measures like rest, medication, and physical therapy, with advanced cases potentially requiring shoulder replacement surgery.

