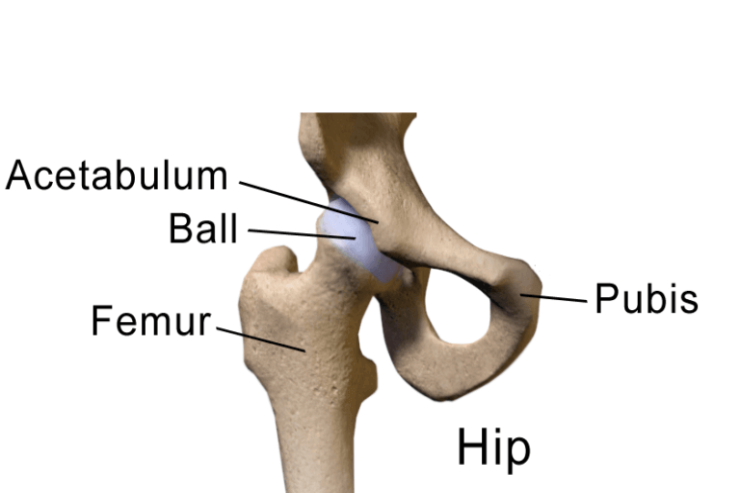
The hip joint, a pivotal ball-and-socket articulation, is formed by the connection between the femur (thigh bone) and the pelvis, comprising the ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. In the Indian population, hip conditions are relatively uncommon. However, certain factors, such as early childhood handling and habitual sitting postures—especially crossing legs—can contribute to hip issues.
Within this joint, a specialized, smooth, and glossy articular cartilage envelops the femoral head and acetabulum, ensuring frictionless movement. Encasing the joint, the synovial membrane—a part of the articular cartilage—maintains joint lubrication for smooth function.
The robust network of ligaments, tendons, and muscles surrounding the joint coalesce to form the joint capsule, essential for stabilizing the bones and averting dislocation. This intricate system works synergistically to uphold the structural integrity of the hip joint.
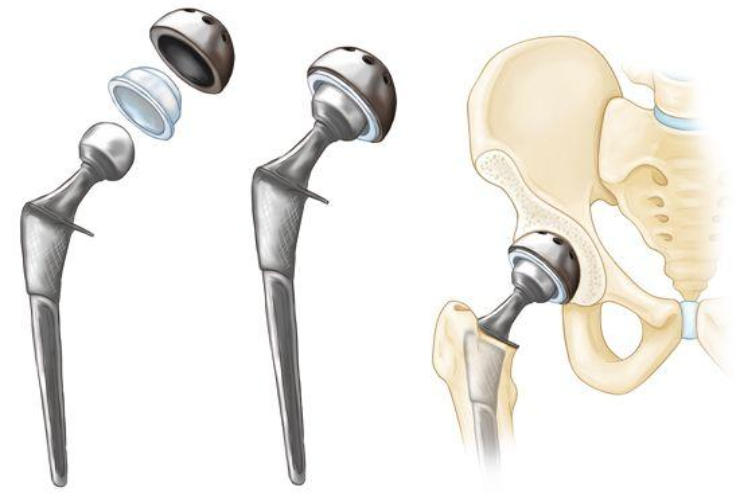
Conditions we treat for Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery is often recommended for individuals experiencing severe hip pain and reduced mobility due to various hip conditions or diseases that affect the hip joint. Some of the common conditions that may necessitate hip replacement surgery include:
Osteoarthritis: This is the most common reason for hip replacement surgery. Osteoarthritis causes the breakdown of cartilage in the hip joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited movement.
Rheumatoid arthritis: A chronic inflammatory condition that can affect the hip joint, causing pain, swelling, and damage to the joint.
Avascular necrosis: This occurs when there is a loss of blood supply to the hip bone, leading to bone death and subsequent joint damage.
Hip fractures: Severe fractures in the hip joint, often resulting from trauma or injury, may require hip replacement surgery, especially in cases where the fracture significantly affects the joint’s integrity.
Ankylosing spondylitis: A type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine but can also lead to inflammation and stiffness in the hip joint.
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH): This is a condition where the hip joint doesn’t form properly, potentially causing instability, pain, and arthritis in later life.
Post-traumatic arthritis: Arthritis that develops following an injury or trauma to the hip joint.
These conditions can lead to persistent pain, limited mobility, difficulty walking, and a reduced quality of life. Hip replacement surgery aims to alleviate these symptoms by replacing the damaged or diseased parts of the hip joint with artificial implants, restoring function and improving the patient’s quality of life.
It’s important to note that the decision to undergo hip replacement surgery is individualized and based on a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, typically an orthopedic surgeon, who considers the patient’s symptoms, medical history, physical examination, imaging studies, and overall health before recommending surgery.
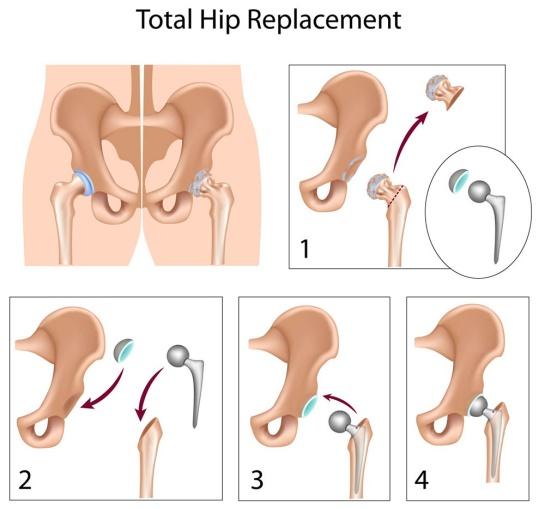
Total HIP Replacement
Hip replacement surgery is often recommended for individuals experiencing severe hip pain and reduced mobility due to various hip conditions or diseases that affect the hip joint. Some of the common conditions that may necessitate hip replacement surgery include The types of hip replacement surgeries based on the materials used for the implant components include:
Metal-on-Polyethylene (MoP):
Metal-on-polyethylene hip replacements involve a metal femoral head that connects with a polyethylene (plastic) liner fitted into the acetabular socket. This combination is among the most commonly used implants in hip replacement surgeries. The metal ball moves against the plastic liner, facilitating smooth movement within the joint.
Ceramic-on-Polyethylene (CoP):
Ceramic-on-polyethylene implants consist of a ceramic femoral head that articulates against a polyethylene (plastic) liner placed in the acetabulum. This combination combines the durability of ceramic material with the low friction properties of plastic, potentially reducing wear compared to metal-on-polyethylene implants.
Ceramic-on-Ceramic (CoC):
Ceramic-on-ceramic hip replacements utilize both a ceramic femoral head and a ceramic liner for the acetabular socket. This combination offers excellent durability, minimal wear, and low friction properties, making it suitable for younger, more active patients. Ceramic-on-ceramic implants are known for their scratch resistance and reduced risk of wear-related complications.

